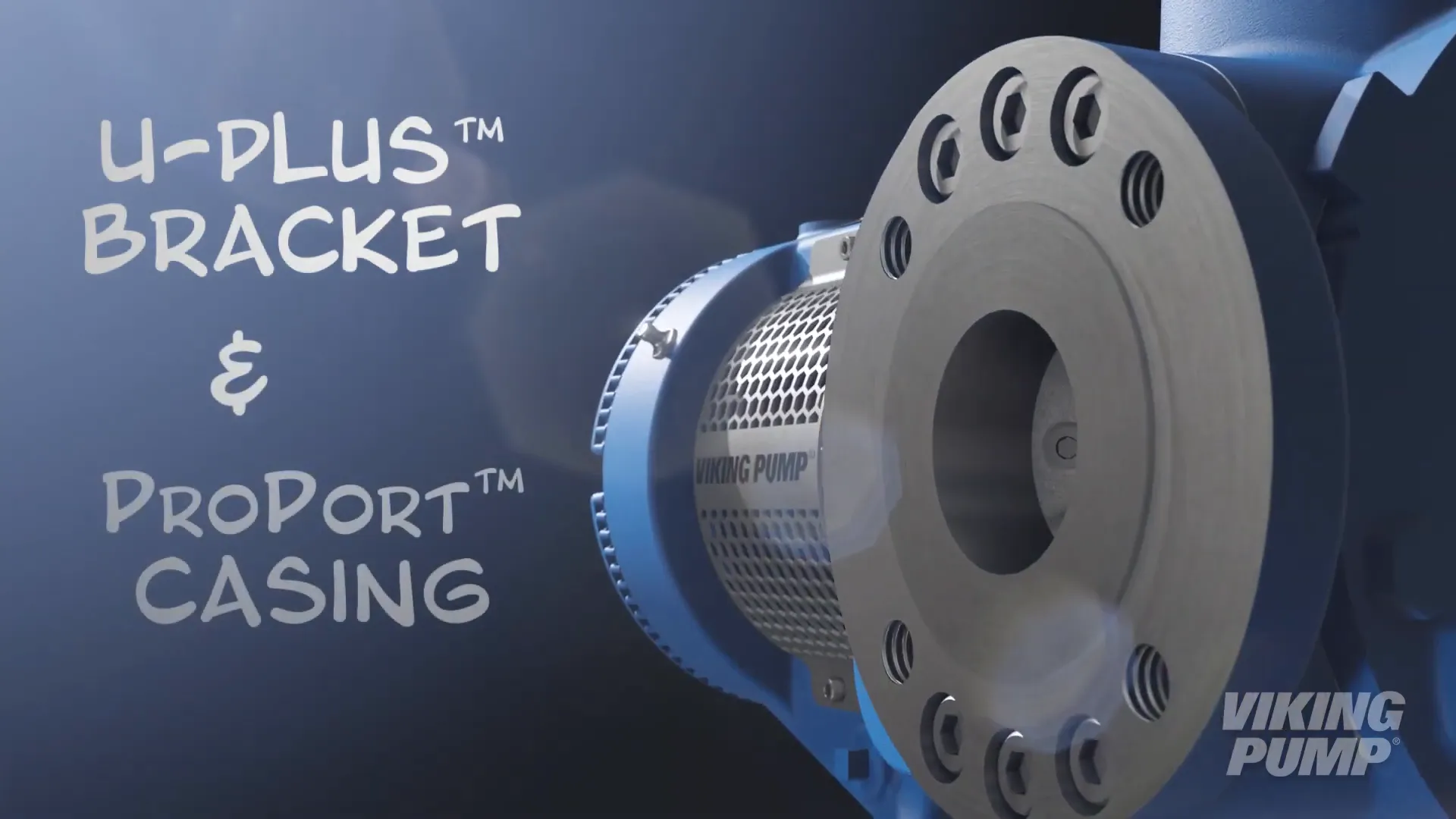
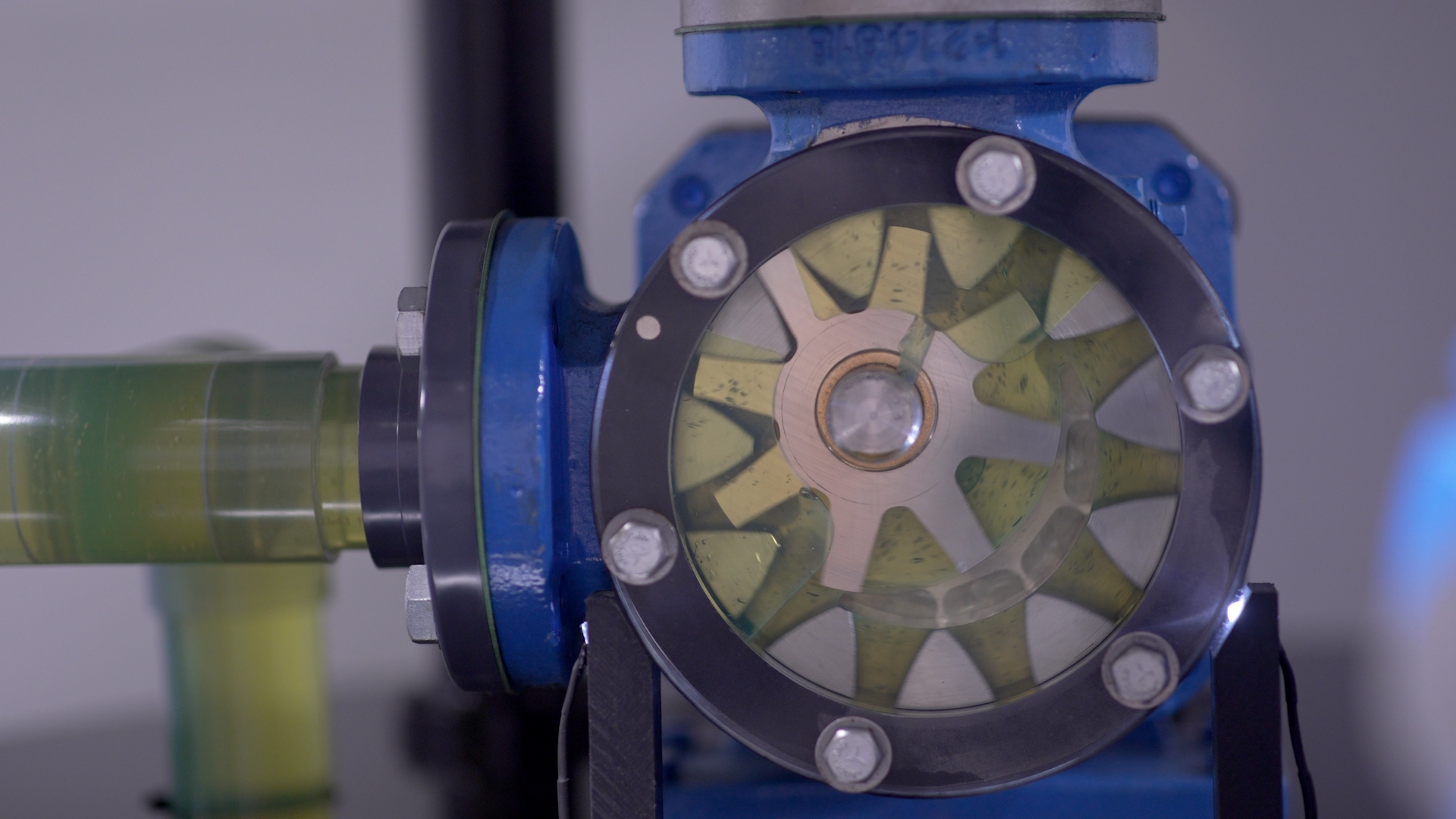
How Pump Jacketing Works - Heating pumps to aid with liquid flow
Solids like chocolate, wax, and asphalt need to be melted prior to being pumped. Jacketing is a common way of heating the pump to successfully transfer these room temperature solids. Pump jacketing consists of chambers that surround the pumping cavity. Heating mediums such as hot oil, water, or steam are pumped into these chambers which then heat the pumping cavity as well as the liquid inside. Once the liquid is melted, the pump can be started. Common pump components that can be jacketed include brackets, heads, rotor bearing sleeves, casings, and relief valves.