Gear Pump (Series)
Glossary Right Side Image

Abbreviation / Acronym
GP
Classification
Definition
An older series of Viking external gear pumps which has been largely replaced by the SG Series™
What is a Viking Pump Gear Pump (GP) pump?
Viking Pump’s “Gear Pump,” or GP, is an older series of external gear pumps which has been largely replaced by the SG Series™.

How do external gear pumps work?
| External gear pumps are similar in pumping action to internal gear pumps in that two gears come into and out of mesh to produce flow. However, external gear pumps use two identical gears rotating against each other. One gear is driven by the motor (driver gear) while the other (driven) gear meshes with and is rotated by the driver gear. | 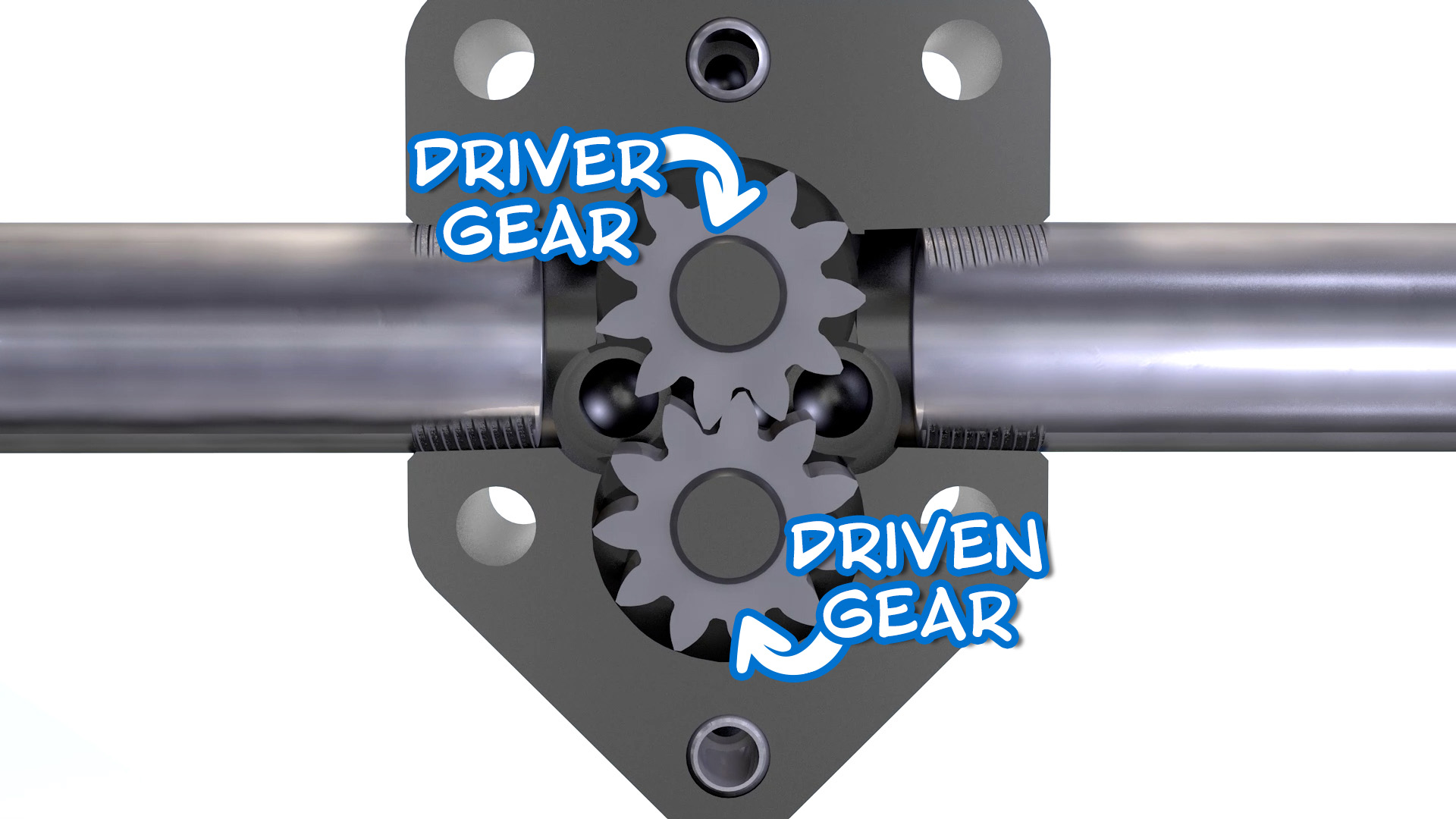 |
| As the gears come out of mesh, they create an expanding volume on the inlet side of the pump. This creates a vacuum which pulls liquid into the pump. Liquid is trapped between the gear tooth cavities and the close fitting casing wall. The rotation of the gears carries the liquid around to the outlet side of the pump. The liquid does not pass between the gears. At the outlet, the meshing of the gears forces the liquid through the outlet port. | 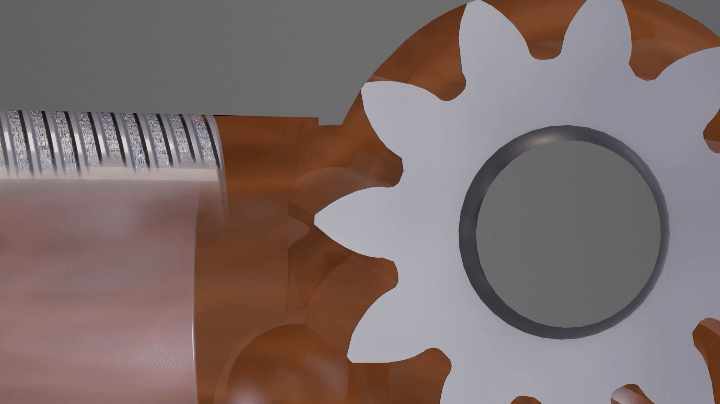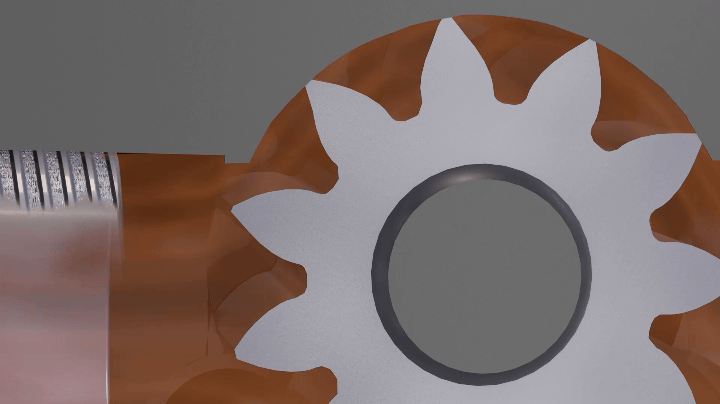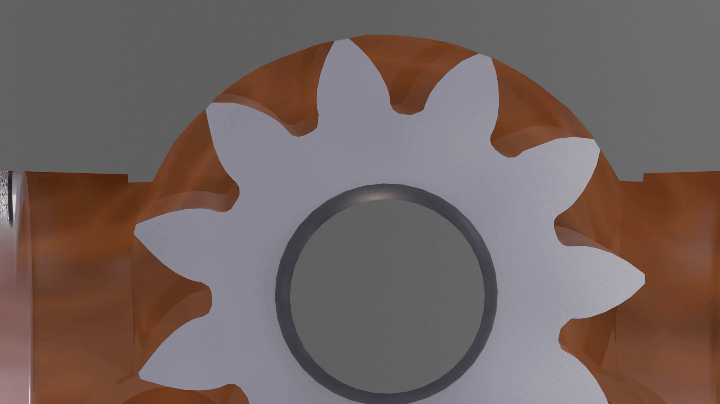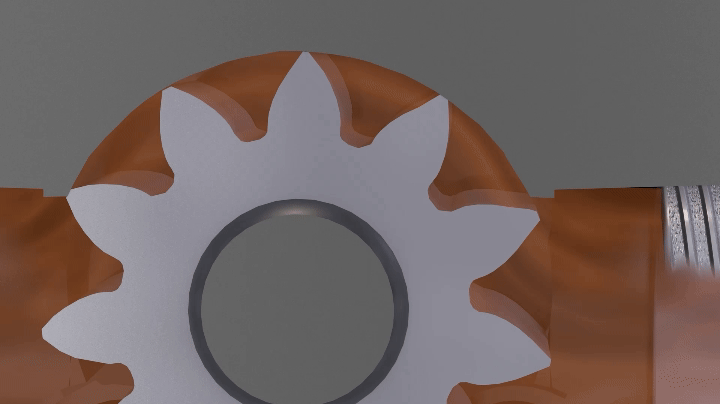 |




