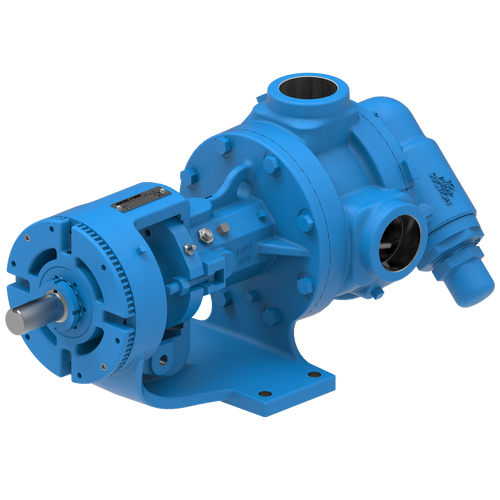
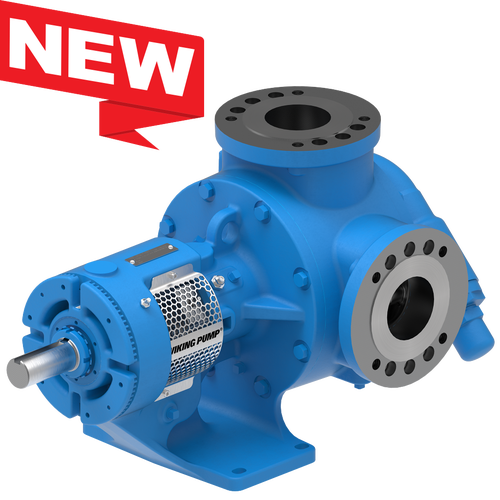
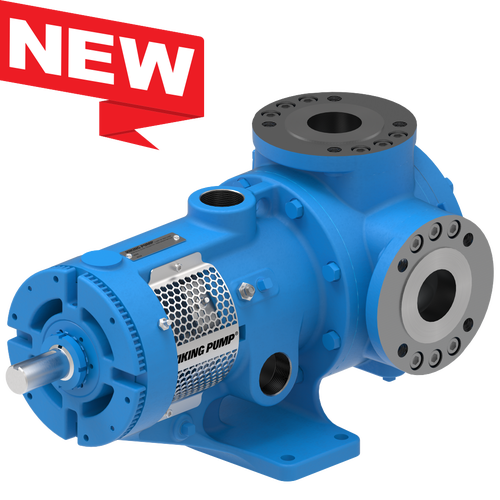
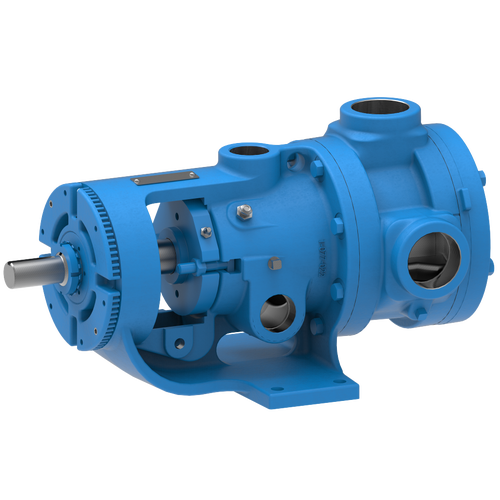
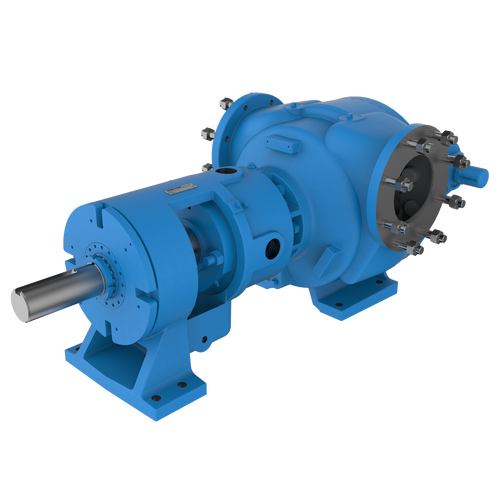
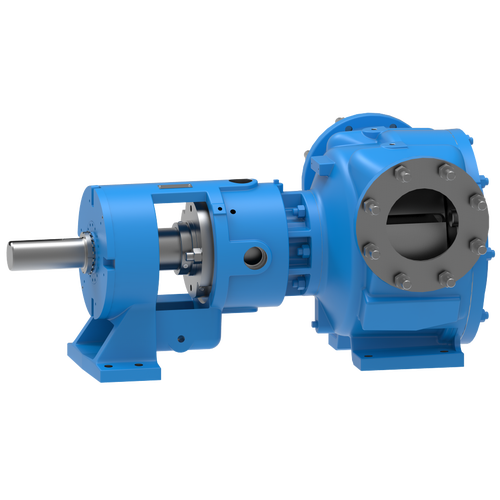
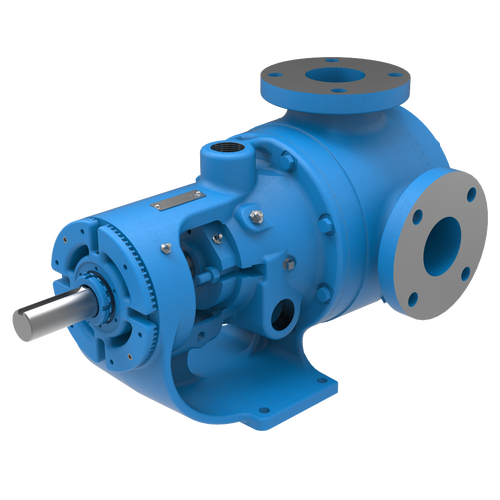
Replace Packing or Mechanical Seals with O-Pro®
Each O-Pro® Seal design option replaces packing or a mechanical seal by occupying the internal bracket cavity with a machined seal gland. Utilizing O-rings to seal externally on the bracket and internally on the shaft, a combination of O-rings and lubricating grease provide a robust seal. This prevents process fluids from leaking out of the pump.
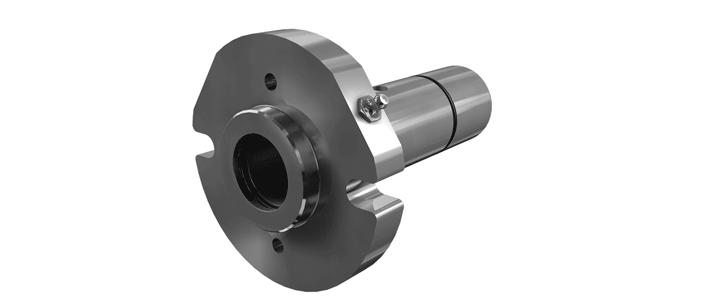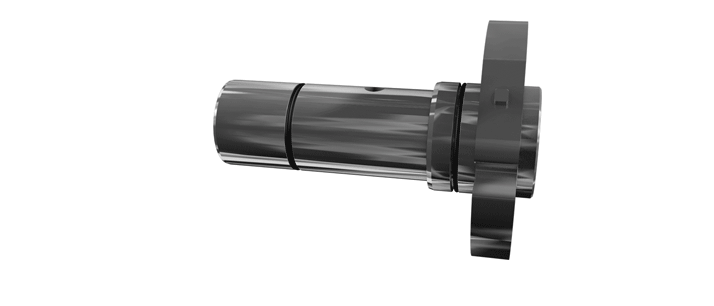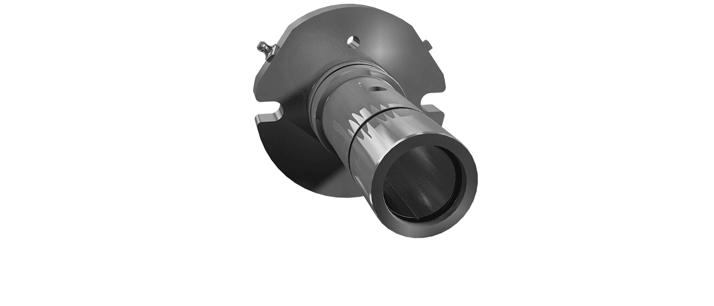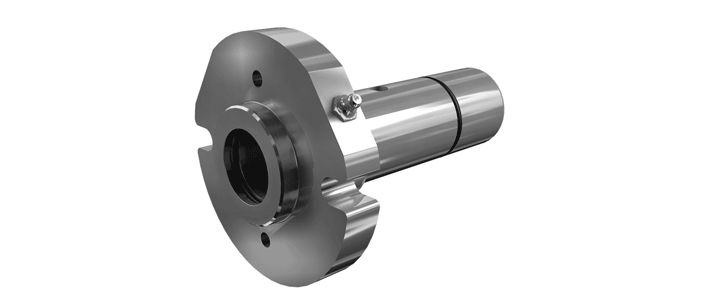
O-Pro® Barrier Seal
The O-Pro® Barrier seal also replaces the bracket bushing - which allows the entire bracket to be sealed off from process liquid.
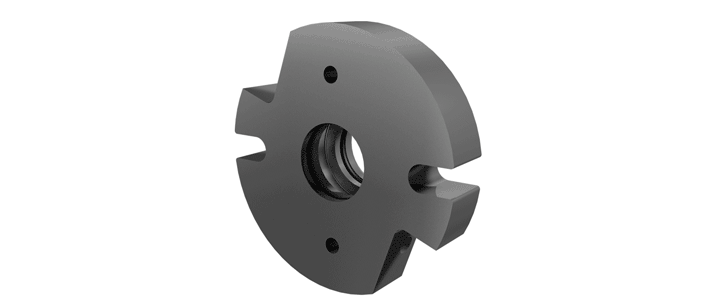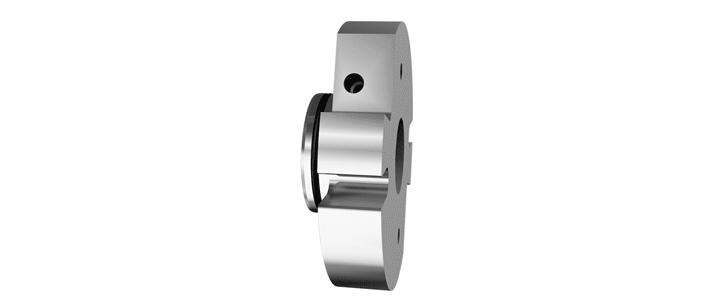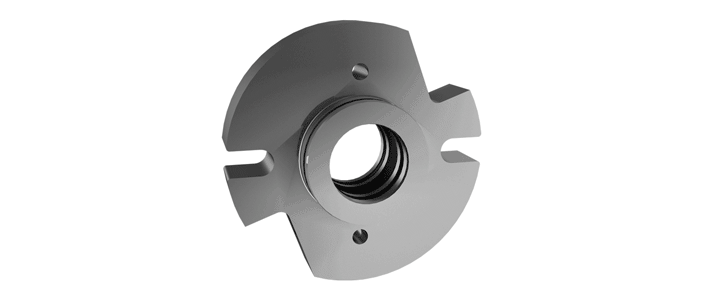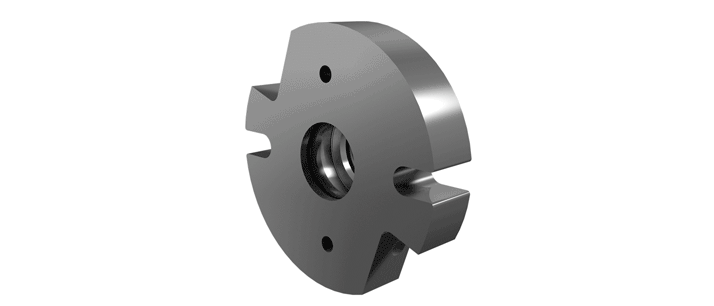
O-Pro® Cartridge Seal
The O-Pro® Cartridge seal allows for an easy retrofit while addressing any need for stainless steel seal construction.

O-Pro® Guard Seal
The stainless steel construction utilizes a sleeve that is secured to the shaft to address any shaft wear concerns to ensure superior performance.
With over 110 years of experience providing positive displacement pumping solutions, Viking Pump has a rich, lengthy history of providing engineered solutions for tough applications. We have dedicated sales and field support specialists who are supported by a team of customer service representatives and engineers. Our knowledgeable team of application engineers available to help with product selection and technical support. USA based company with vertically integrated manufacturing facility.
FACTORY TESTED
Our state-of-the-art testing equipment is used to confirm performance prior to shipments. Our world-class lab gives Viking Pump the ability to test our pump designs across a range of relevant variables.