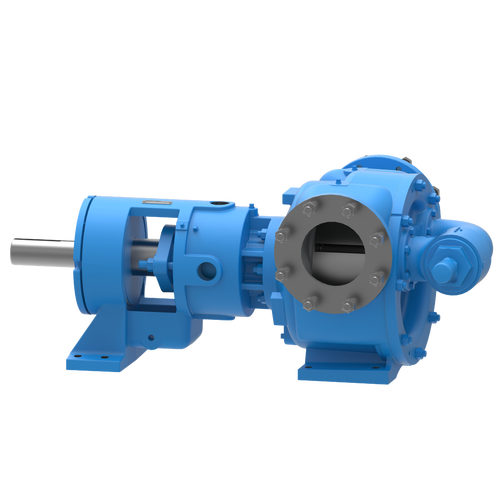
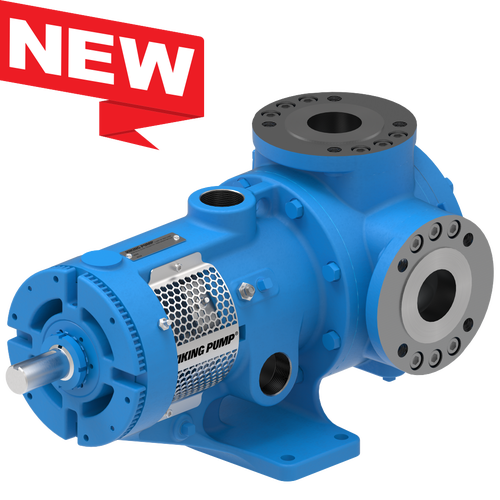
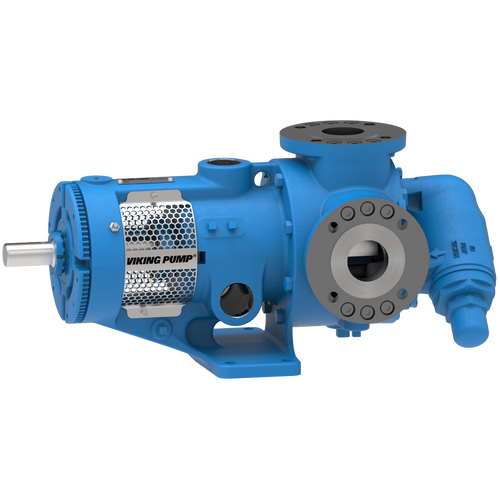
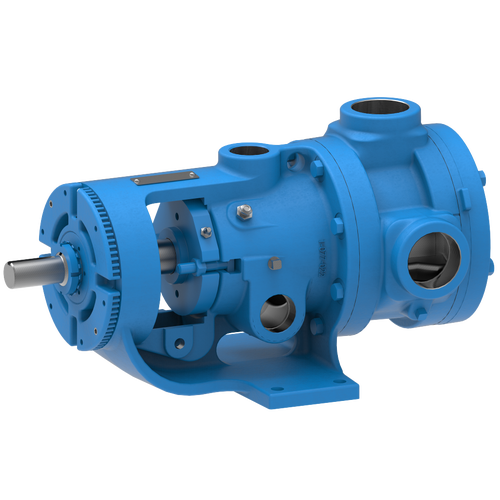
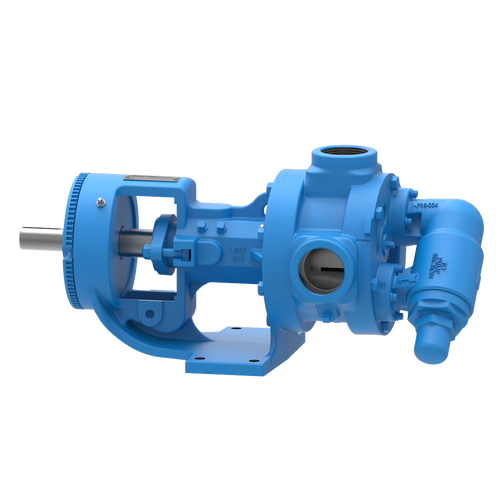
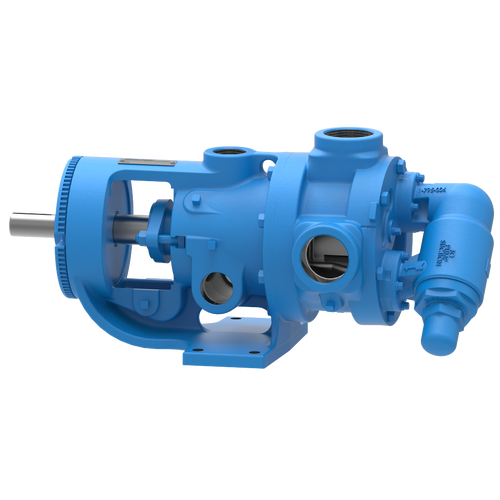
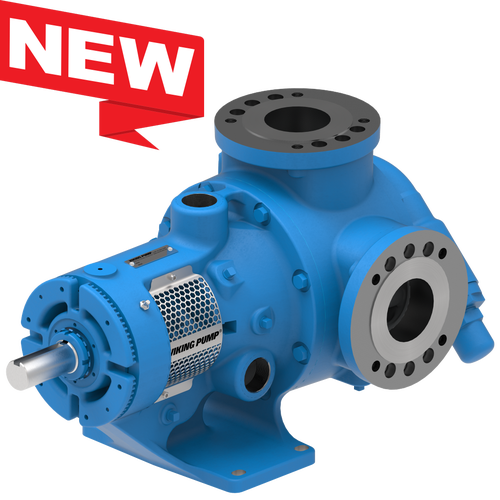
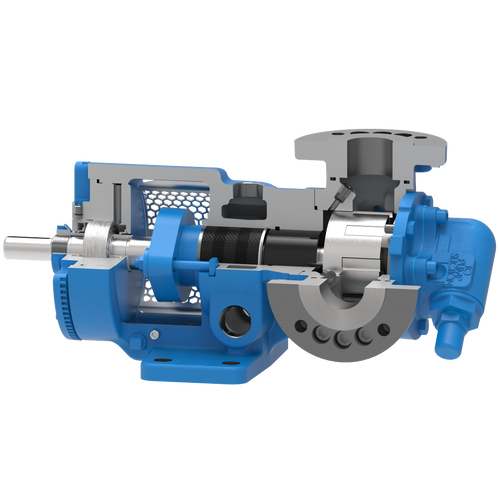
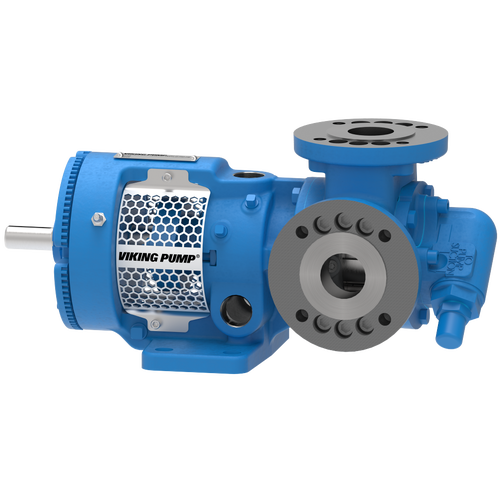
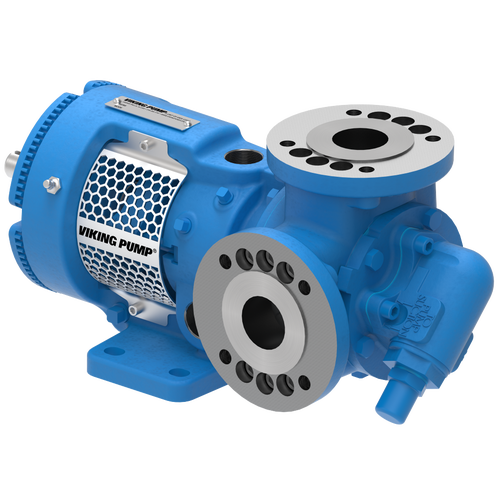
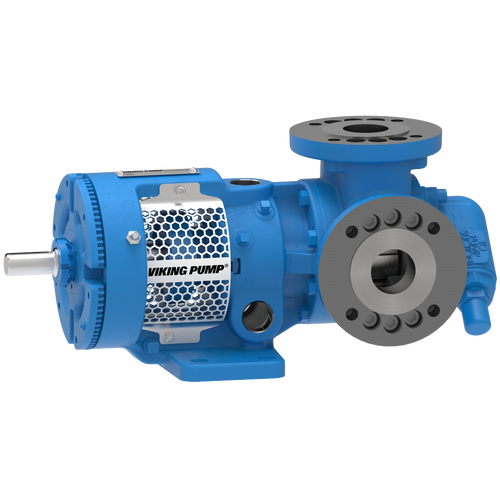
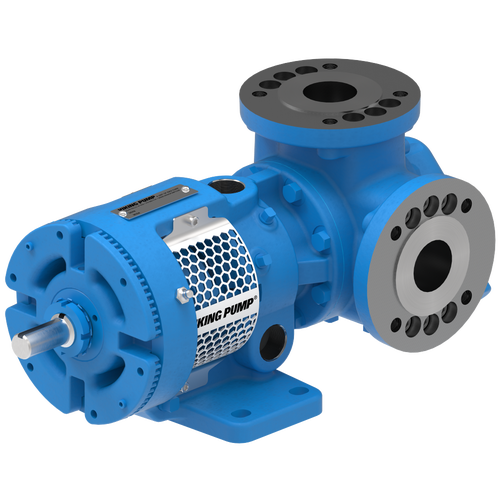
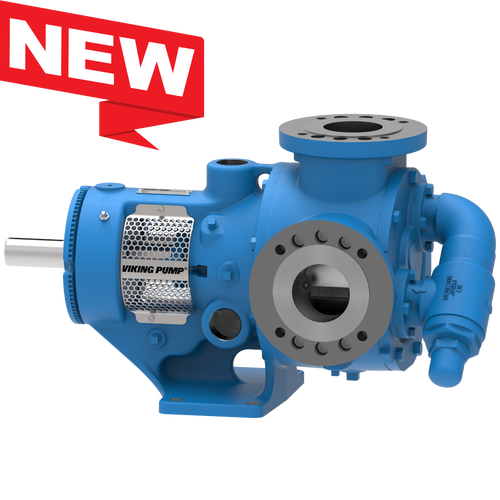
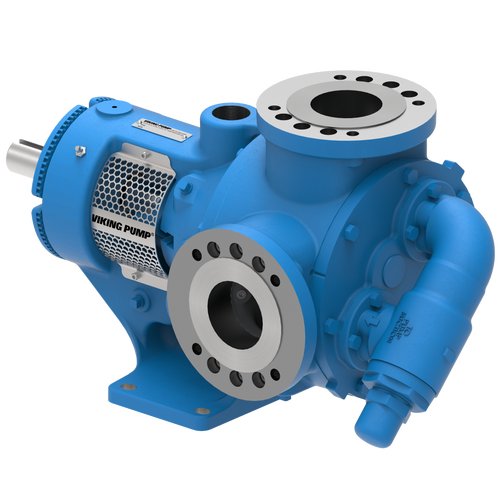
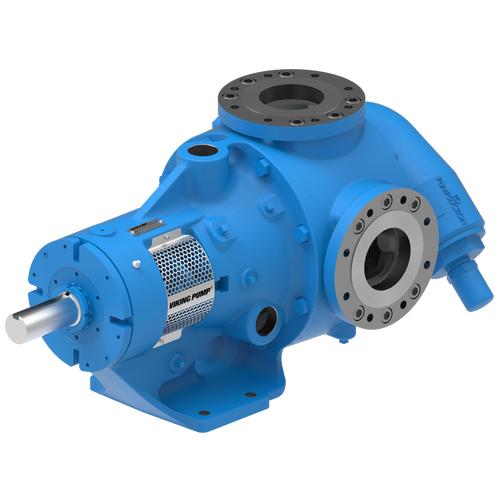
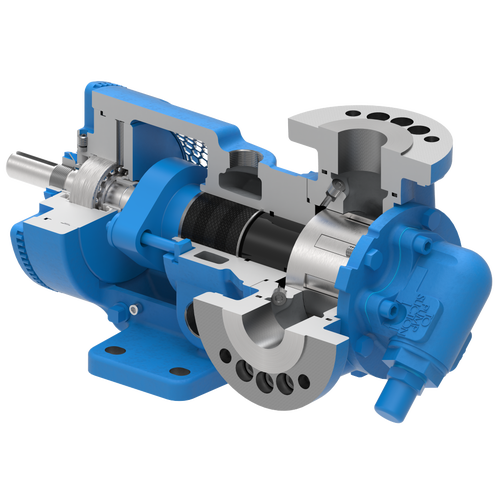
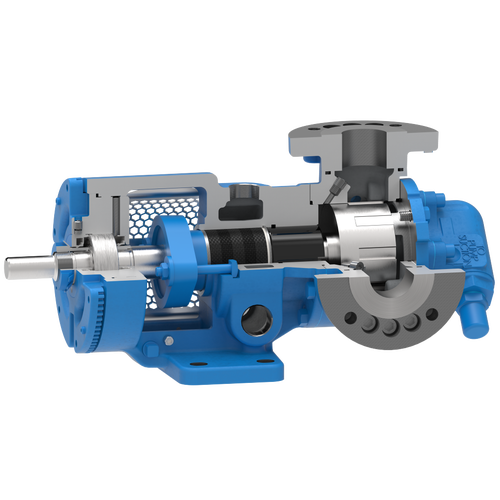
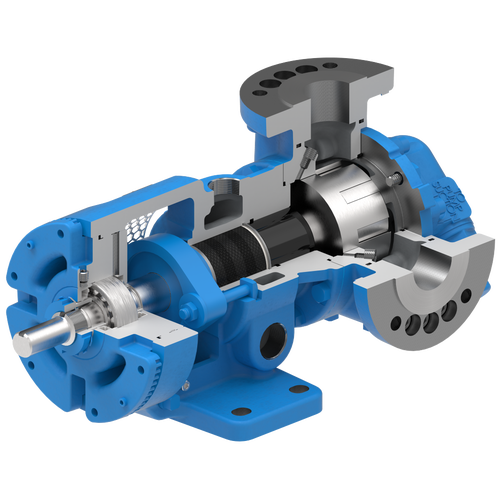
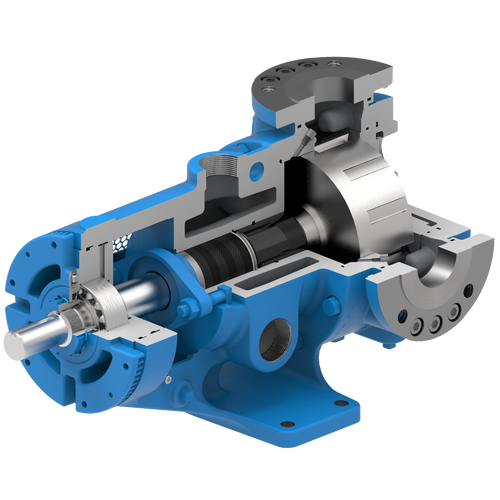
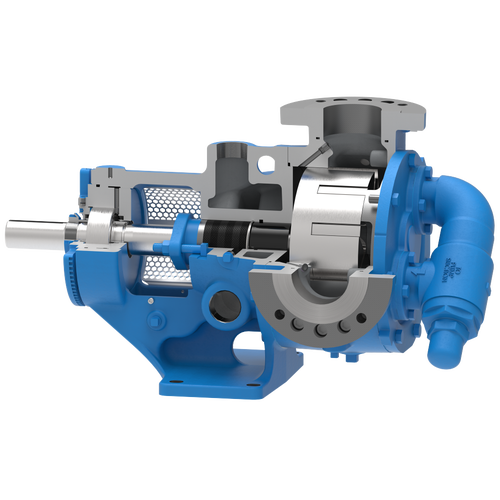
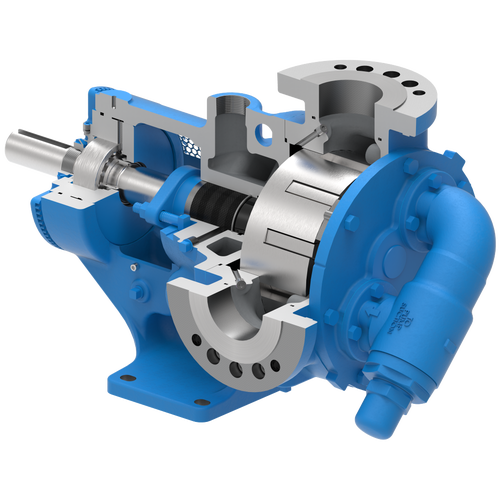
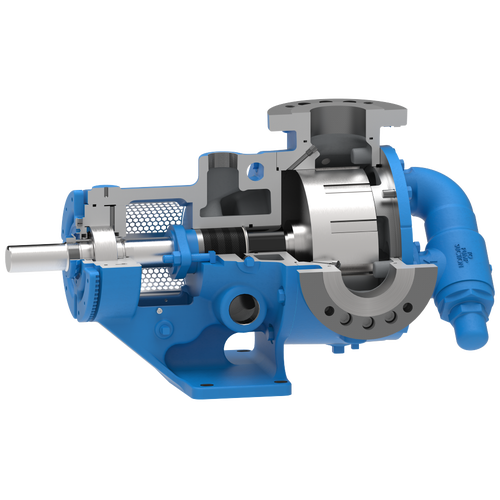
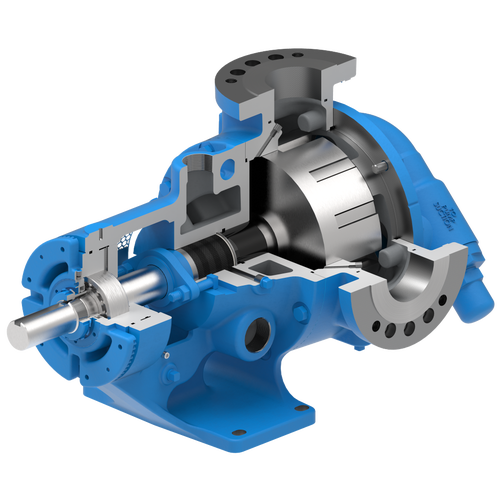
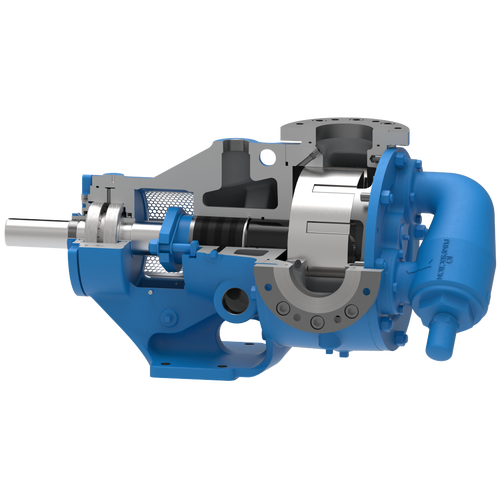
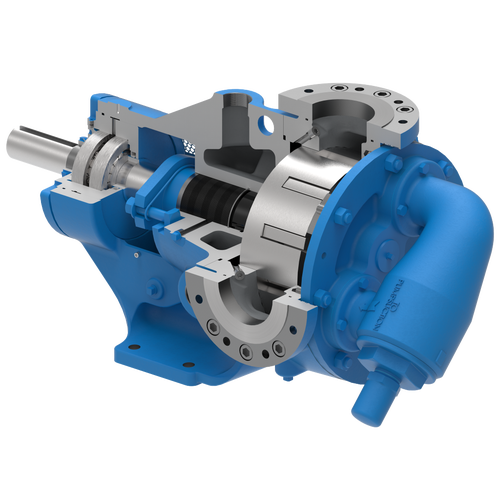
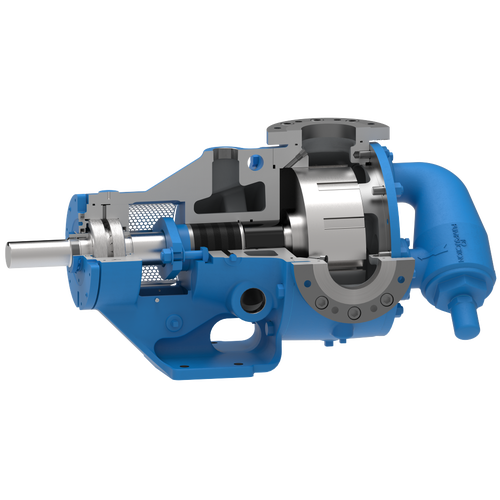
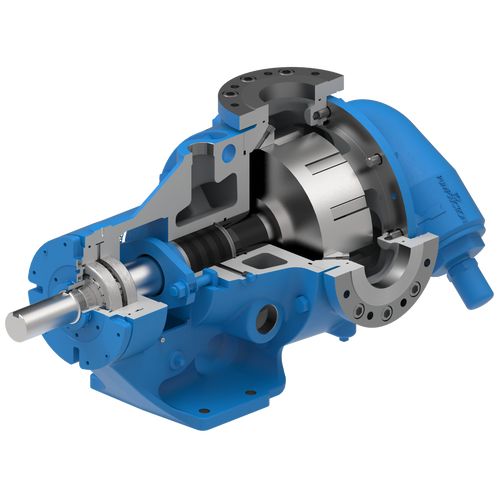
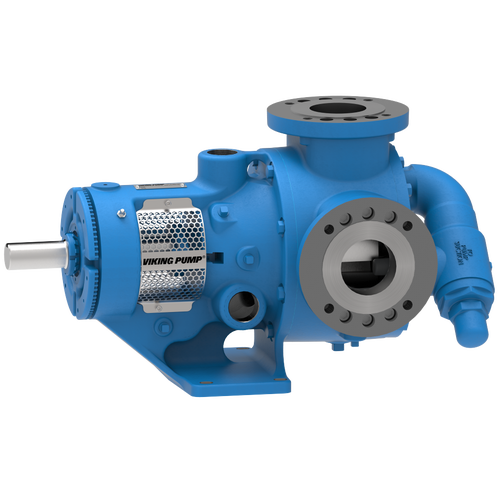
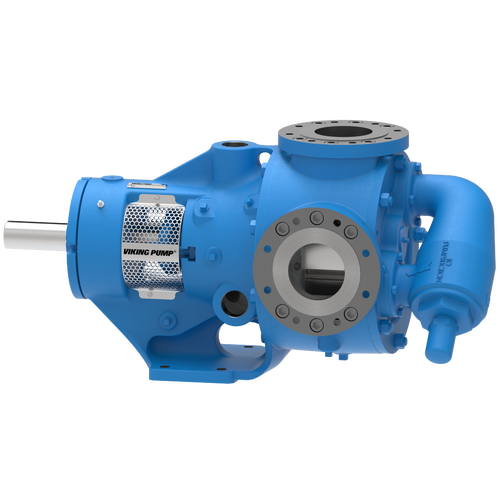
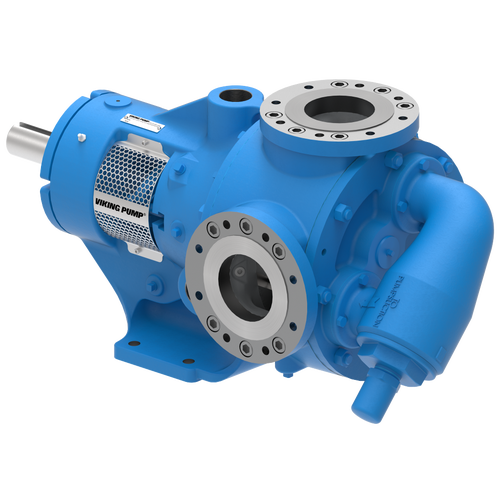
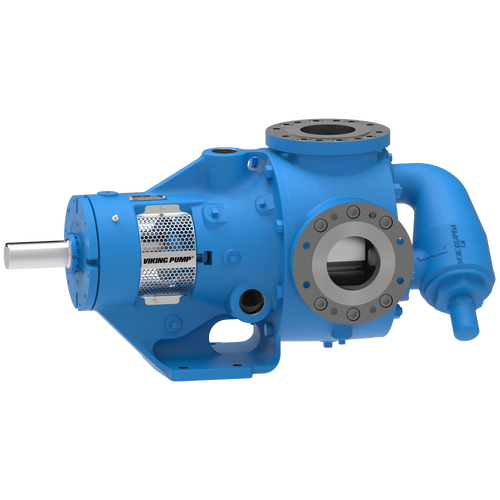
The 227C Series™ internal gear stainless steel pump is the flexible, simple, and adaptable solution for a wide range of applications. This new generation of pumps comes standard with internal jacketing, the U-Plus™ bracket sealed with packing, as well as the ProPort™ casing that accommodates a variety of port sizes and types depending on your needs. It can handle flow rates up to 320 GPM (73 m³/h).
Features & Benefits
- All stainless steel construction for corrosion resistance over a wider pH range
- ProPort™ casing utilizes mounting pads on each port designed to fit a variety of different flange types and sizes, enabling flexibility when connecting pumps to piping
- U-Plus™ bracket, available on H-QS sizes, offers seal location to be in the stuffing box or behind the rotor
- Integral jacketed chambers in bracket and head allow pumps to maintain constant temperature and consistent product flow
-
Opposite porting on all pump sizes available

Capacity
to 320 GPM
to 73 m³/h
Viscosity
28 to 2,000,000 SSU
0.1 to 440,000 cSt
Pressure
to 150 PSI
to 10 BAR
Temperature
-120°F to +500°F
-85°C to +260°C
Options
Porting
Drives
Mounting
Sealing
Specifications
| Model | Standard Port Size | Nominal Pump Rating (GPM) | Nominal Pump Rating (m3/h) | Maximum RPM | Maximum Pressure PSI | Maximum Pressure BAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H227C | 1.5 | 10 | 1.9 | 1150 | 150 | 10 |
| HL227C | 1.5 | 20 | 3.7 | 1150 | 150 | 10 |
| K227C | 2 | 50 | 11 | 520 | 150 | 10 |
| KK227C | 2 | 65 | 15 | 520 | 150 | 10 |
| L227C | 2.5 | 100 | 23 | 520 | 150 | 10 |
| LL227C | 3 | 135 | 31 | 520 | 150 | 10 |
| LS227C | 3 | 160 | 36 | 520 | 150 | 10 |
| Q227C | 4 | 200 | 45 | 350 | 150 | 10 |
| QS227C | 6 | 320 | 73 | 350 | 150 | 10 |
Photos









Videos









High Fructose Corn Syrup (HFCS)
High Fructose Corn Syrup (HFCS) is usually followed by the percentage of fructose in the liquid, ranging from 42 to 55%. It is most commonly used in soft drinks, jams, and jellies as a sweetener. Temperature regulation is relevant because discoloration of the liquid could occur at elevated temperatures.

Lecithin
Lecithin is a mixture of triglycerides, fatty acids, and carbohydrates that typically ranges in viscosity up to 5000 SSU, but may be more viscous depending on make-up and temperature. It is typically derived from soybean oil but may also be obtained from egg yolks, corn, or other vegetable seeds.